Download Primary Radar Training and Experiment Guide
1 RADAR FUNDAMENTALS
2 THE BASIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A RADAR
2.1 The directionality of the radiation
2.2 Pulse width
2.3 Beam width
2.4 The radiation power and receiver sensitivity
2.5 Pulse repetition rate, and the rotation speed of the antenna
2.6 Maximal range
2.7 The resolution of the radar in range
2.8 The resolution of the radar in azimuth
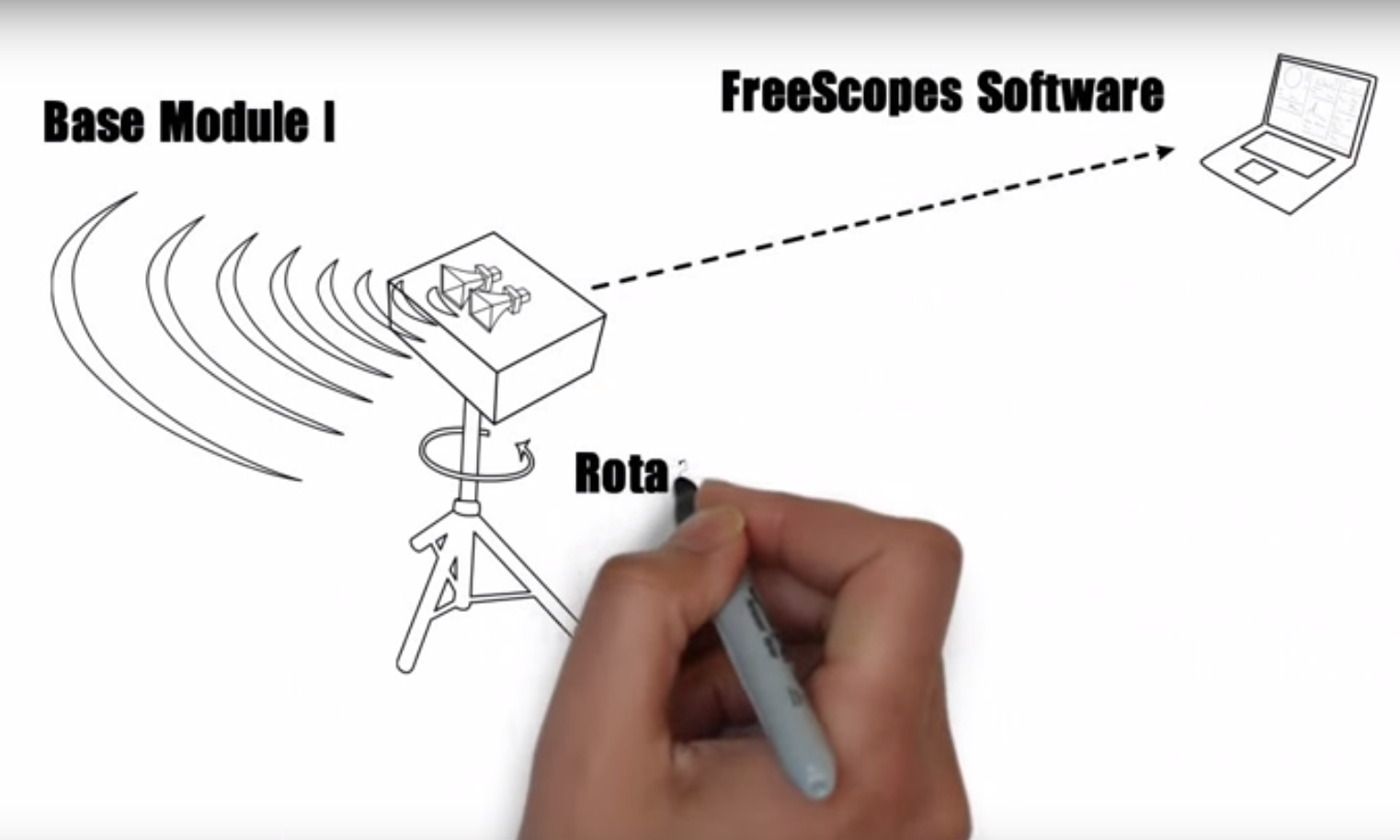
3 BASIC CONTROLS OF THE PSR SIMULATOR
3.1 Elements of the radar windows for in the Controller Work Position CWP
3.2 Elements of supervisor window for Pseudo Pilot Position control
4 EXAMPLES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF PULSE RADARS ILLUSTRATED WITH THE PSR PULSE SIMULATOR
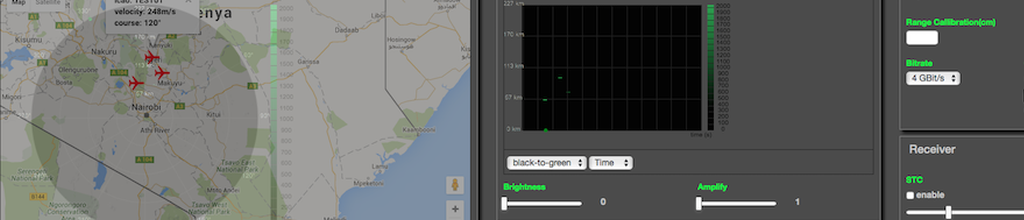
4.1 Determination of the distance and direction between radar and aircraft as well as between aircrafts
4.2 Working in conditions of interference from terrain
4.3 Accomplishing the ideal resolution
4.4 Effect of the signal power and noise to radar performance
4.5 RCS fluctuation and using polarization changing for decreasing of effect
4.6 Signal attenuation
4.7 TASKS FOR SELF-PACED LEARNING
5 EXAMPLES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF CW RADARS ILLUSTRATED WITH THE CW (DOPPLER) SIMULATOR
5.1 Using the Doppler radar to discriminate the targets by the speed
6 EXAMPLES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF FMCW RADARS ILLUSTRATED WITH THE FMCW SIMULATOR
6.1 Revisiting the example of two overlapping aircrafts
6.2 Impact of Doppler shift on FMCW radar
6.3 Velocity impact to FMCW
6.4 Determining of the radial speed from radar with non-triangular modulation
7 EXAMPLES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADARS ILLUSTRATED WITH THE SAR SIMULATOR
7.1 Creating a high resolution SAR-image
8 EXAMPLES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF INVERSE SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADARS ILLUSTRATED WITH THE iSAR SIMULATOR
8.1 Creating a high resolution iSAR-image