The Decepetion Package I enhances the SkySim radar simulator by integrating various jammers. Paired with FreeScopes, including the FreeScopes Defense modules Disturbance & Filtering and Analysis I & II, it enables practical training in countermeasures against electronic warfare attacks.
Included jammers are:
The jammers in the simulated jamming environment are able to match the following radar characterstics:
The simulator for Jammers can emulate Noise Jammers and Deception Jammers.
The scope of exercises in the fields which can be implemented with the DSP radar simulator is virtually unlimited. So we just state some fields of application here:
Detection of Jamming with "classical" methods
(FreeScopes series Basic I&II and ATC I&II are required)
Defense against Disturbances with intelligent algorithms
(FreeScopes series Disturbance Filtering & Analysis needed)
Barrage jamming spreads energy across a wide frequency range. Such a jamming of an attacked radar requires high power to achieve a continuous coverage of various frequencies. Given the jammer's fixed total radiation power, this technique lowers the radars general efficiency as it leads to a low power density. But this technique is efficient when attacking radars which can vary their frequencies or radars which operate with several frequencies concurrently.
A workaround to the barrage jammer's low efficiency is spot jamming. Spot jammers jam in a narrow band, hence with a higher power density. Consequently it can raise the jamming signal power over a narrower frequency spectrum.
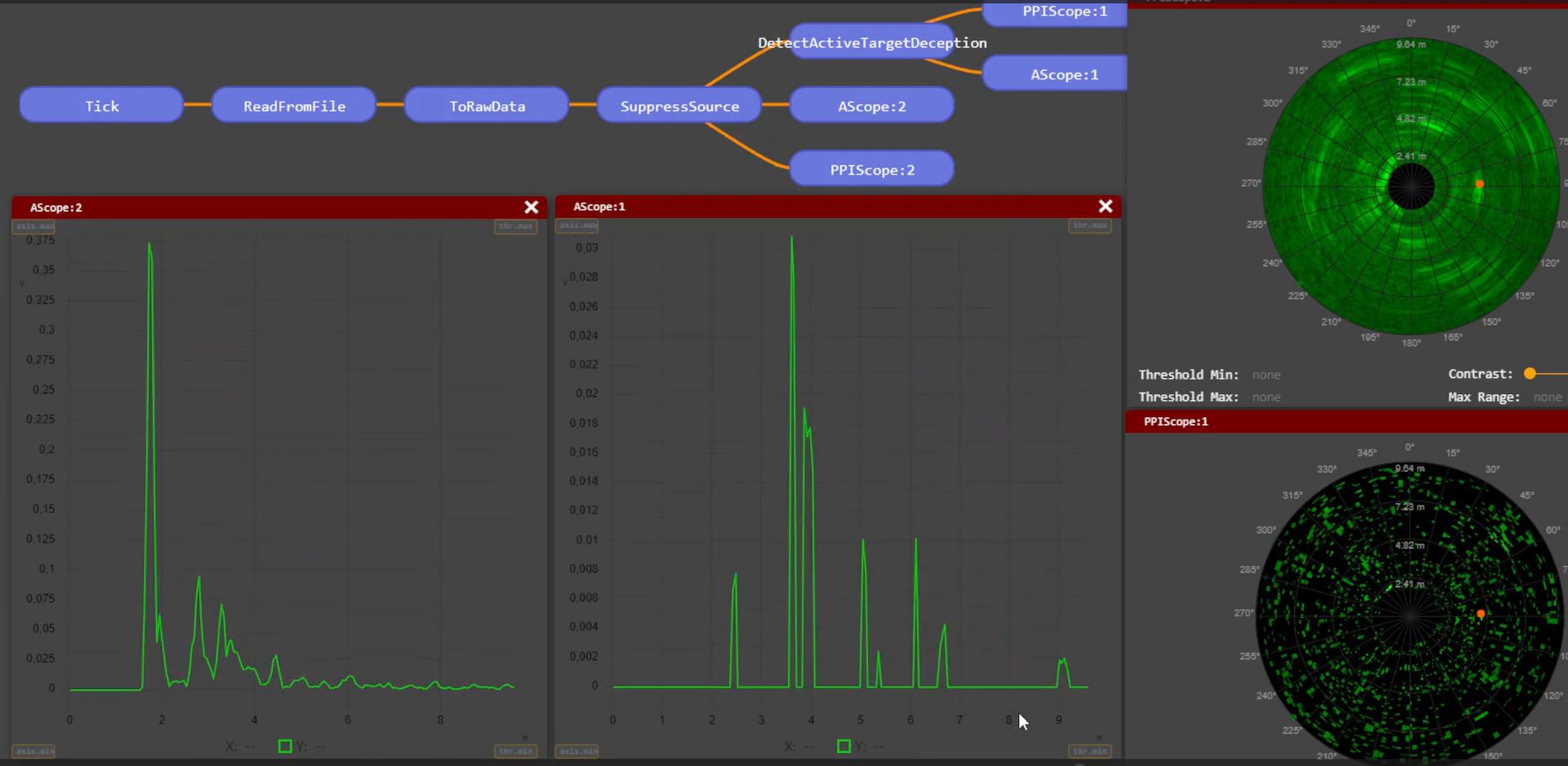
An active target operates as a simplistic form of a reactive jammer. It detects radar pulses, amplifies them, and retransmits them after a slight delay caused by the cable length and the electronic components involved. This results in the surveillance radar perceiving the amplified pulse at a greater distance than the original target. The purpose of this amplification is to diminish the reflectivity of the actual target to below the clutter level, effectively masking its presence.
The simulated active target works comparably to SkyRadar's hardware jammer.
Range deception is created through DRFM jammers, which are placed on intruding aircraft or drones. Digital Radio Frequency Memory (DRFM) jammers digitally capture and retransmit RF signals. In the case of range deception, they delay or advance the "reflected" signal. First the DRFM creates a cover pulse over the real target's reflection. It is much higher than the reflection of the real target. The surveillance radar reduces the gain in this range gate with electronic circuits at the radar receiver, in order to control the amplitude of the covered pulse. We call this Automatic Gain Control (AGC). The consequence of this cheat: the real target disappears below clutter level.
Range Gate Pull-Off (RGPO) is an electronic countermeasure technique used to deceive radar systems by gradually increasing the delay of the returned echo signal. This creates the illusion that the target is moving away from the radar, causing the radar's tracking gate to follow the false target and lose lock on the actual target. RGPO effectively disrupts the radar's ability to accurately track and engage the target.
SkyRadar's base unit is a close range training and research radar for indoor and outdoor experiments.
At the leading edge of security provision within its key markets, Cryptomathic closely supports its global customer base with many multinationals as longstanding clients.
SkyRadar develops innovative radar training solutions and simulation systems, empowering education, research & professional training in aviation and defense sectors.
All rights reserved by SkyRadar 2008 - 2025


SkyRadar Consortium
Email: sales@SkyRadar.com | Website: www.SkyRadar.com | © [2025] SkyRadar