Aeronautical Information Service in digital form represent the Aeronautical Information Management Concept. AIM is the integrated management of AIS data.
 The increasing growth of air traffic around the globe has placed immense pressure on the efficient exchange of accurate and timely information.
The increasing growth of air traffic around the globe has placed immense pressure on the efficient exchange of accurate and timely information.
Such information must be structured in a way that supports system-wide interoperability. To be a part of the vision for secured seamless information access and exchange System Wide Information Management has emerged as a key concept. The exchange of flawless information is achieved through interoperable systems.
Aeronautical Information service handles information that is vital for the safety, economy, regularity, and efficiency of air navigation services.
Aeronautical Information Service is a paper-centric environment that is based on charts and paper-based publications. The present Aeronautical Information Service environment lacks even a single data set. Information exists in paper or form base. AIS generates paper-based products. There exist various data issues in this environment.
The publications commonly encounter periodical errors as well as problems regarding timely dissemination to meet the regulations. Only nonstandard data quality requirements prevail. This results in probable hindrance along the data chain. Hence this paper’s product-centric environment is required to evolve into a completely data-centric environment. As today along with increasing traffic, standards for air navigation have changed drastically with a breakthrough in technological advancement.
More advancement brings more sophisticated tools. Those paper-based products and documentation cannot withstand this era of digitalization and automation. System-Wide Information Management is based on universal infrastructure, regulations, and governance of information related to Area Navigation Services as well its seamless exchange with all the stakeholders. The seamless exchange has been made possible through the inclusion of open standards and mainstream web technologies. The exchange is done through interoperable services.
 Interoperability is simply the ability of systems to exchange data with each other and use the data that has been exchanged without any hindrance. SWIM incorporates information exchange models to acquire syntactic interoperability.
Interoperability is simply the ability of systems to exchange data with each other and use the data that has been exchanged without any hindrance. SWIM incorporates information exchange models to acquire syntactic interoperability.
The main feature of syntactic interoperability is the established connection between systems. Through this connection, data is seamlessly exchanged across the systems.
When data is exchanged through the data exchange model another aspect is required to meet is a semantic interpretation of the data being exchanged.
Once the data is exchanged the content of data should remain the same as well as its interpretation by a system installed at the sender as well as at the receiver end. Even in presence of a human operator to interact the understanding of information or data should remain the same.
The open standards for information exchange include the following:
- AIXM (Aeronautical Information Exchange Model)
- AXXM (Weather Exchange Model)
- FIXM (Flight Information Exchange Model)
The AIXM is an exchange model designed to enable the provision of Aeronautical Information in digital format. The flow of aeronautical data is complex as it is connected to various stakeholders that include data suppliers as well as data consumers. These include data providers, data integrators, aircraft manufacturers, airlines, operators, etc.
AIXM supporting the transition from AIS to AIM
The Aeronautical Information Exchange Model introduces syntactic interoperability by establishing a connection between systems under use by different stakeholders. Through this connection, data is exchanged across the systems in a seamless.
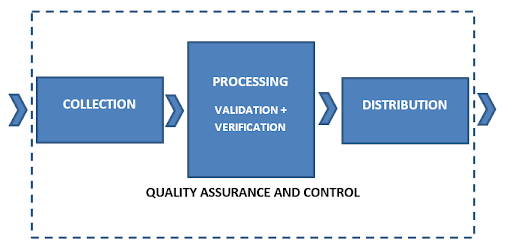
AIXM provides an XML-based schema for coding aeronautical data in a standardized manner. Therefore, it can be considered a standard-based approach when it comes to managing aeronautical data. It collects aeronautical data from various data originators. While collecting data the main emphasis is on clear roles and metadata as defined by the standards. The collection of data is of prime importance as it ensures smoothness in customization by ensuring the prevalence of standardized data. How data will be coded and how it will be customized to meet standard requirements for AIXM.
After that data has been collected it is processed rigorously based on the defined standards. AIXM while processing data validates it based on metadata. Any obvious inaccuracy is identified through a plausibility check of the data. When data is collected it is required to be checked for errors. Because of these errors transmitted and received data may vary in terms of interpretation. This happens during transmission for multiple reasons data portions get corrupted. During data processing errors in bits of data are identified by the application of the Cyclical Redundancy check. This verification process ensures the integrity of data.
Dissemination of data is done through interoperable services and systems. The whole AIXM system acquires its quality assurance by ensuring data traceability and data integrity. Quality control is employed by error detection during the verification process. Various compliance standards act as a filter to reinstate quality control. These compliance standards may pertain to product specifications or data quality as a whole.
Service-oriented architecture in ATM incorporates AIXM as an interoperable logical model for the exchange of specified data.
Based on the above-stated facts it becomes clear that AIXM supports the transition from AIS to AIM by incorporating the concept of interoperability, data quality, standardization, and service-oriented programming. It helps not only in promoting digital automation but also opens the horizon for the incorporation of future innovations and upgrades.
Aeronautical Information Management can be considered as a digital Aeronautical Information Service. The data is available in digital standard format instead of paper-based publication in a format that isn’t universal everywhere. AIM onwards acquire connection with System Wide Information Management which incorporates AIM digital concept. That is an exchange of aeronautical digital data across the logical model with systems.
Aeronautical Information Management Concept helps in ensuring different systems are working in coherence with each other. This embedded system allows having an automated airspace view as a whole without the intervention of humans. This is an important milestone in the aviation industry. It just does not remain confined to present standards and concepts to meet the current aviation demand. This concept has been designed through such proper planning that it also opens the horizon for future concerns. Whether this concern relates to changing trends in technology or an increase in traffic density requiring more sophisticated tools. With time, more systems are going to be part of this whole system strengthening and increasing the capacity of the system. With increasing capacity, its application and functions will keep on increasing and providing an increasing return to the aviation industry.ng increasing return to the aviation industry.
AIS and SkyRadar's Tower Simulator
AIS is part of SkyRadar's Radar and Tower simulator. Talk to us to learn more.
References
- ICAO DOC 8126 Aeronautical Information Services Manual
- ICAO ANNEX 15 Aeronautical Information Service
- ICAO DOC 10039 Manual on System Wide Information Management (SWIM) Concept.
- The Implementation of Aeronautical Information Exchange Model in SWIM (2021), by Bingjie Ren & Yuanchun Jiang