Air Traffic Control (ATC) is a critical component of modern aviation, responsible for the safe and efficient movement of aircraft. ATC relies on accurate and reliable transmission of data between various components of the system.
One common cause of transmission errors in ATC systems is related to the encoder. This article will explore the impact of transmission media errors due to the encoder in ATC, the factors responsible for such errors, common types of transmission media errors caused by the encoder, and steps that can be taken to prevent and rectify such errors.
Definition of Transmission Media Error due to Encoder
An encoder is a device that converts a physical position or motion into an electrical signal that can be transmitted to other components of the ATC system. Transmission media errors due to the encoder can occur when there is a mismatch between the electrical signal transmitted by the encoder and the signal received by the receiver. This can lead to errors in the data transmitted, potentially compromising the safety and efficiency of ATC operations.
What is an Encoder? Explain with an Example
An encoder is a device that converts a physical position or motion into an electrical signal. In the context of ATC, encoders are used to measure the altitude and airspeed of aircraft. For example, an altitude encoder may be installed on an aircraft to measure its altitude, and the electrical signal generated by the encoder is transmitted to the ATC system. The ATC system uses this information to track the location of the aircraft and ensure that it is maintaining a safe altitude.
Factors Responsible for Encoder Related Transmission Media Errors
Several factors can contribute to encoder-related transmission media errors in ATC systems, including:
Interference
Electrical interference can disrupt the signal transmitted by the encoder, leading to errors in the data received by the receiver.
Misalignment
A misalignment between the encoder and the receiver can cause errors in the data transmitted.
Calibration
If the encoder is not properly calibrated, it can lead to errors in the data transmitted.
Faulty Equipment
Faulty equipment can cause errors in the data transmitted by the encoder.
Some Common Types of Transmission Media Errors Caused by Encoder
Some common types of transmission media errors caused by the encoder include:
Data Loss
Data loss can occur when the electrical signal transmitted by the encoder is disrupted, leading to missing or incomplete data.
Data Corruption
Data corruption can occur when the electrical signal transmitted by the encoder is distorted or interfered with, leading to inaccurate data.
Data Delay
Data delay can occur when the electrical signal transmitted by the encoder is delayed, leading to delayed or inaccurate data.
Impact of Encoder Related Transmission Errors on Air Traffic Control Services
The impact of encoder-related transmission errors on ATC services can be significant. These errors can compromise the safety and efficiency of ATC operations, potentially leading to delays, flight cancellations, or even accidents. For example, if an altitude encoder fails to transmit accurate data, the ATC system may not be able to track the location of the aircraft accurately, leading to potential safety risks.
A scenario that illustrates the impact of transmission errors related to Encoder on Air Traffic Control Services
Scenario 1: Encoder Transmission Error
Imagine a busy air traffic control tower, the air traffic controllers were diligently managing the flow of airplanes in the sky. However, an unexpected transmission error related to the encoder occurred, disrupting the exchange of critical flight data.
Impact on Air Traffic Control Services
Inaccurate Flight Information
The encoder is responsible for transmitting essential flight data, including the aircraft's position, altitude, and speed. With a transmission error in the encoder, the data received by air traffic controllers becomes unreliable or distorted. This can lead to inaccurate information about the location and status of aircraft, making it challenging for controllers to make informed decisions and ensure safe aircraft separation.
Reduced Situational Awareness
The encoder's transmission error affects the radar displays and other systems used by air traffic controllers to monitor and track aircraft. As a result, controllers experience reduced situational awareness, as they struggle to maintain a clear picture of the airspace. This can lead to delays in providing instructions to pilots, increased workload for controllers, and a higher risk of potential conflicts or unsafe conditions.
In this scenario the transmission error related to the encoder hampers the exchange of critical flight data, leading to inaccurate information and reduced situational awareness for air traffic controllers. This, in turn, compromises their ability to ensure safe and efficient air traffic control services.
Scenario 2: Data Loss due to Encoder Transmission Error
In another air traffic control tower, the air traffic controllers were diligently monitoring and guiding aircraft through the skies. However, an encoder transmission error occurred, resulting in the loss of crucial flight data during transmission.
Impact on Air Traffic Control Services
Loss of Real-time Flight Tracking
The encoder plays a vital role in transmitting real-time flight data to air traffic controllers. With a transmission error causing data loss, controllers are unable to track aircraft positions accurately and efficiently. This lack of real-time flight tracking can lead to confusion, delays in response, and difficulty in maintaining safe separation between aircraft.
Impaired Decision-making
Accurate flight data is essential for air traffic controllers to make informed decisions in managing air traffic flow. The loss of data due to the encoder transmission error hampers their ability to assess the current situation and respond promptly to changing conditions. This can result in delays, inefficient rerouting of aircraft, and potential safety risks.
In this scenario the encoder transmission error causing data loss significantly impacts the air traffic control services by hampering real-time flight tracking and impairing decision-making capabilities. The lack of accurate flight information creates challenges for controllers in managing air traffic flow effectively and ensuring the safety of aircraft in the airspace.
Steps to be Taken by ATSEP in Rectification of Transmission Media Errors Related to Encoder
When Air Traffic Safety Electronics Personnel (ATSEP) encounter transmission media errors related to an encoder, they can follow the steps outlined below to rectify the issue:
Identify the symptoms
Determine the specific symptoms or indications that suggest transmission media errors related to the encoder. This could include data loss, corrupted data, inconsistent data transmission, or any other abnormalities that affect the encoder's performance.
Analyze the system
Gain a thorough understanding of the encoder system's specifications, configuration settings, and operational requirements. Review the encoder's documentation, including manuals, technical specifications, and any relevant guidelines or procedures. Identify the potential causes of transmission media errors.
Check the transmission media
Inspect the transmission media used by the encoder, such as cables, connectors, fiber optics, or wireless links. Look for any physical damage, loose connections, or other issues that may affect the quality of the transmission. Rectify any identified problems, such as replacing damaged cables or connectors.
Verify encoder settings
Review the encoder's settings and configuration to ensure they are optimized for the specific transmission media. Check the encoding parameters, modulation schemes, bit rates, or other relevant settings to ensure they are compatible with the transmission media's capabilities.
Perform diagnostic tests
Utilize diagnostic tools and techniques to analyze the encoder's performance and identify transmission media errors. This can involve using specialized software, test equipment, or built-in diagnostic features of the encoder. Collect relevant data on transmission quality, error rates, or other performance indicators.
Troubleshoot and isolate
Based on the diagnostic results, identify the specific areas or components that may be causing the transmission media errors. This could include issues with the encoder's hardware components, software modules, interface configurations, or external factors influencing the transmission media. Troubleshoot each potential cause systematically to identify and isolate the root cause of the problem.
Rectify the issue
Once the root cause is identified, take appropriate actions to rectify the transmission media errors related to the encoder. This may involve repairing or replacing faulty hardware components, reconfiguring software settings, adjusting interface parameters, or optimizing the encoder's setup to improve transmission quality.
Test and validate
After rectifying the transmission media errors, conduct thorough testing to ensure that the encoder is now transmitting data without errors. Use appropriate test procedures, simulated scenarios, or real-world scenarios to validate that the encoder is operating correctly and transmitting data reliably through the transmission media.
Document the resolution
Document the entire process, including the symptoms, diagnostic results, troubleshooting steps, and the final resolution. This documentation serves as a reference for future maintenance, troubleshooting, or knowledge sharing within the ATSEP team.
It's important to note that the specific steps and procedures may vary depending on the type of encoder, the transmission media used, and the organization's guidelines. ATSEPs should follow the prescribed guidelines and procedures provided by their organization and stay updated with the latest industry best practices for rectifying transmission media errors related to the encoder.
To prevent encoder-related transmission media errors, Air Traffic Safety Electronics Personnel (ATSEP) can follow the steps outlined below
Understand the system
Gain a thorough understanding of the encoder system's specifications, configuration settings, and operational requirements. This includes knowledge of the encoder's capabilities, supported transmission media, and any relevant standards or guidelines.
Select appropriate transmission media
Choose the transmission media that is most suitable for the encoder system and the specific requirements of the communication network. Consider factors such as data rate, distance, environmental conditions, and reliability. Select transmission media that can handle the bandwidth and signal quality requirements of the encoder.
Install and configure transmission media properly
Follow proper installation procedures for the chosen transmission media. Ensure that cables, connectors, fiber optics, or wireless links are installed correctly and securely. Adhere to recommended cable routing and grounding practices. Verify that the transmission media is properly configured and compatible with the encoder's specifications.
Implement appropriate cable management
Use proper cable management techniques to organize and protect cables connected to the encoder. This includes routing cables away from sources of interference, using cable trays or conduits to avoid damage, and labeling cables for easy identification and troubleshooting.
Ensure signal integrity
Take measures to maintain the signal integrity during transmission. This includes minimizing signal attenuation, reflections, or electromagnetic interference. Use appropriate shielding, grounding techniques, and cable specifications to reduce the impact of external factors on the signal quality.
Perform regular maintenance
Establish a regular maintenance schedule to inspect and maintain the transmission media and associated components. This includes checking for physical damage, loose connections, or degradation of the transmission media. Regularly clean connectors, inspect cables for wear and tear, and perform any necessary repairs or replacements.
Monitor transmission quality
Implement a system for monitoring the quality of the transmission media. This can involve using monitoring tools, analyzing error rates, signal strength, or other performance metrics. Monitor for any anomalies or deviations from normal transmission quality and investigate and address them promptly.
Conduct periodic testing
Perform periodic testing of the transmission media to ensure its integrity and performance. This can include conducting link quality tests, signal-to-noise ratio measurements, or bit error rate tests. Testing can help identify any degradation or issues with the transmission media early on and allow for timely corrective actions.
Keep software and firmware up to date
Ensure that the encoder's software and firmware are up to date. Regularly check for updates from vendors and apply the latest patches, bug fixes, and performance enhancements. Updated software and firmware can address known issues and improve the encoder's compatibility and reliability with the transmission media.
Document and learn from incidents
Document any incidents or transmission media errors that occur and conduct a thorough analysis to understand the root causes. Learn from these incidents to improve the system's design, configuration, or operational procedures and implement preventive measures based on the lessons learned.
By following these steps, ATSEPs can help prevent encoder-related transmission media errors, ensure optimal performance, and maintain reliable communication systems. It's important to note that the specific steps and procedures may vary depending on the type of encoder, the transmission media used, and the organization's guidelines. ATSEPs should follow the prescribed guidelines and procedures provided by their organization and stay updated with the latest industry best practices for preventing encoder-related transmission media errors.
Factors Responsible for Encoder-related Transmission Media Errors
Several factors can contribute to encoder-related transmission media errors. Some of the common factors include:
Wiring Issues
Poorly installed or damaged wiring can result in errors in the transmission of data from the encoder.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
EMI can cause errors in the transmission of data from the encoder to the ATC system. EMI can be caused by various factors such as nearby radio transmitters, other electrical equipment, or wiring issues.
Poor Signal Quality
Poor signal quality can result in incorrect data being transmitted from the encoder to the ATC system.
Component Failure
Failure of components such as capacitors or resistors in the encoder can lead to errors in the transmission of data.
Research Highlights
Increased Error Rates
Transmission media errors, when introduced by encoders, can lead to an increase in the overall error rates of data transmission within air traffic control systems. These errors can affect critical information, such as aircraft positions, trajectories, and communication data, potentially compromising the safety and efficiency of air traffic operations.
Degraded System Performance
The presence of transmission media errors can result in degraded system performance within air traffic control systems. Errors in the transmitted data can cause delays, inaccuracies, and inconsistencies in the information received by air traffic controllers, leading to reduced situational awareness and decision-making capabilities.
Impact on Communication
Transmission media errors can affect the communication systems used by air traffic controllers to interact with pilots and other stakeholders. Errors in encoded data can lead to distorted or incomplete messages, hindering effective communication and coordination between air traffic controllers and pilots, potentially introducing misinterpretations or misunderstandings.
Compromised Surveillance
Encoders play a crucial role in providing accurate surveillance data to air traffic control systems. Transmission media errors can impact the integrity of this surveillance data, resulting in inaccurate or delayed information about aircraft positions and movements. This can increase the risk of collisions, reduce the effectiveness of conflict detection systems, and hinder efficient air traffic management.
Mitigation Strategies
Research suggests the implementation of various strategies to mitigate the impact of transmission media errors due to encoders. These include error detection and correction techniques, redundant transmission paths, improved signal processing algorithms, real-time monitoring and diagnostics, and the use of fault-tolerant architectures.
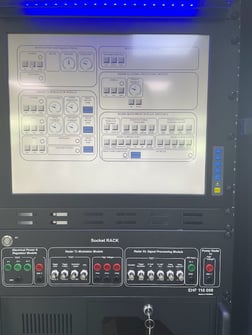
SkyRadar's System Monitoring & Control Solution
SkySMC - SkyRadar’s System Monitoring and Control Suite is a pedagogically enhanced, fully operational monitoring & control tool. It has been designed to practice these use cases. We have optimized it to host ATSEP training in SUR, NAV, COM, DPR and SMC compliant to EASA's Easy Access Rules for ATM-ANS (Regulation (EU) 2017/373) and ICAO Doc 10057.
SkyRadar provides SkySMC as a complete laboratory in a turn-key approach, or as a virtual infrastructure (for purchase or as a service).
SkySMC is not a simulator, but a fully operational open monitoring system. It comes by default with a server including various virtualized applications and virtualized servers, but also connects to simulated systems. In addition, there are various hardware extensions available including training infrastructures, monitorable training radars, or even complete ATM systems, all connected to the System Monitoring & Control solution. Most components such as the radars, it IT infrastructure or networks exist in hardware and software (virtualized or simulated).
The two photos above show the same trouble-shooting panel and socket rack in real hardware and in the simulator (fully functioning).
SkyRadar's System Monitoring & Control training system can be easily blended into distance learning solutions and existing learning management systems.
Let's talk
Stay tuned to be always the first to learn about new use cases and training solutions in ATSEP qualification (real radars or simulators).
Or simply talk to us to discuss your training solution.
References
-
National Transportation Safety Board. (2018). Aviation Accident Final Report - Loss of Control on Approach Ameristar Air Cargo, Inc. dba Ameristar Charters, Inc. Flight 9363 Boeing MD-83, N786TW. https://www.ntsb.gov/investigations/AccidentReports/Reports/AAR1802.pdf
-
National Transportation Safety Board.(2017). Aviation Accident Preliminary Report - Loss of Control in Flight Arkansas Aircraft Charter, LLC Piper PA-28-180, N4925L. https://www.ntsb.gov/_layouts/ntsb.aviation/brief.aspx?ev_id=20171107X73916&key=1
-
Federal Aviation Administration.(2019). AC 20-171A - Standardized Procedures for Maintaining Air Traffic Control Communications. https://www.faa.gov/documentLibrary/media/Advisory_Circular/AC_20-171A.pdf