UPS-related power source errors have a significant impact on ATC, leading to potential disruptions in communication, radar systems, and critical equipment. See the details and learn how SkySMC can be used to train ATSEP on this use case.Power source errors due to UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) related issues can have a significant impact on air traffic control (ATC) operations. These errors can lead to communication disruptions, radar outages, and equipment malfunctions, posing risks to safety and operational efficiency. Understanding the consequences of such errors is crucial in implementing effective measures to mitigate their impact and ensure uninterrupted ATC services.
Definition of Power Source Issues due to UPS Related Errors
Power source errors due to UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) related issues refer to the failures or malfunctions in the backup power system that is designed to provide continuous and uninterrupted electrical supply to critical equipment in case of a main power outage. These errors can include issues such as battery failure, faulty components, improper maintenance, or inadequate capacity, which can lead to disruptions in power supply and potentially impact the operations of air traffic control systems.
What is UPS Related Error? Explain with an example related to ATSEP and Air Traffic Control Service
UPS-related errors refer to issues or malfunctions that occur within an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) system. A UPS is a backup power source used to provide uninterrupted electrical power to critical equipment and systems, such as those used in air traffic control (ATC) services.
One example of a UPS-related error in the context of ATSEP (Air Traffic Safety Electronics Personnel) and ATC services could be a battery failure within the UPS system. The UPS relies on its batteries to supply power during electrical outages or fluctuations. If a UPS battery fails, it can lead to a loss of backup power, potentially causing a disruption in critical ATC systems, such as radar displays, communication equipment, or surveillance systems. This can result in temporary service interruptions and affect the ability of ATC personnel to effectively monitor and manage air traffic, potentially compromising safety and operational efficiency.
ATSEPs play a crucial role in maintaining and troubleshooting UPS systems in ATC facilities. It is their responsibility to regularly inspect, maintain, and replace UPS batteries and other components to minimize the risk of UPS-related errors. By ensuring the proper functioning of UPS systems, ATSEPs contribute to the reliability and continuous operation of essential ATC services.
Training Scenarios illustrating the impact of Power Source Issues related to UPS related errors on Air traffic Control Services
Scenario 1: UPS Failure during a Power Outage
 In a bustling air traffic control center, there is a sudden power outage due to an external power source error. The center is equipped with an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) system designed to provide backup power during such situations. However, due to a UPS-related error, the backup power fails to kick in, leaving the control center without any electricity.
In a bustling air traffic control center, there is a sudden power outage due to an external power source error. The center is equipped with an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) system designed to provide backup power during such situations. However, due to a UPS-related error, the backup power fails to kick in, leaving the control center without any electricity.
In this scenario, the loss of power disrupts critical systems and equipment, including communication systems, radar systems, and surveillance systems.
Air traffic controllers are left in the dark, unable to effectively communicate with pilots, monitor aircraft movements, or manage airspace. The lack of power severely impacts the ability to ensure safe and efficient air traffic control services, leading to widespread flight delays, confusion, and potential safety hazards.
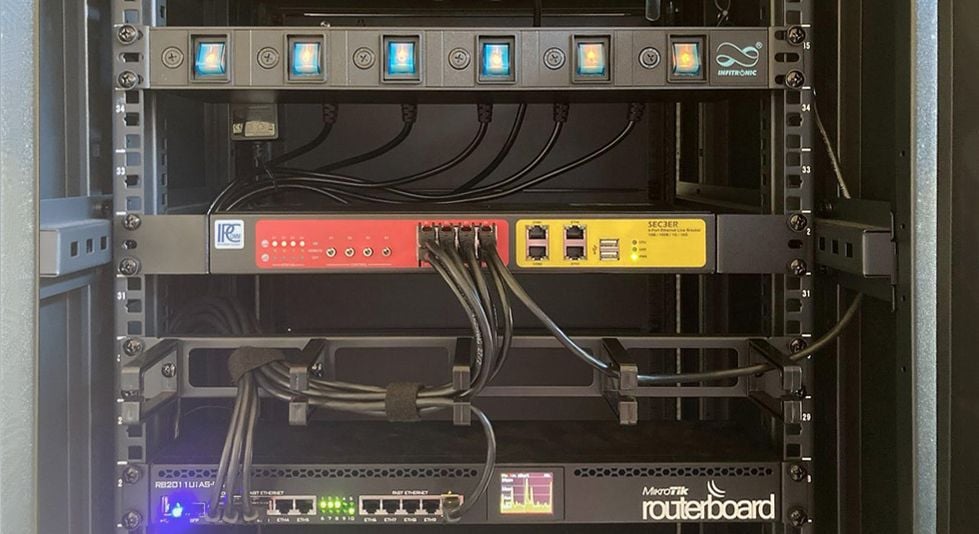

SkyRadar's SkyRack offers a set of 2 redundant UPS. The upper image shows the 2 UPS mounted at the bottom of the cabinet. The backside in the photo below shows how the teacher can manipulate the architecture through switches in power supply and network to degrade its functioning.
Scenario 2: Inadequate UPS Capacity during a Power Surge
In another air traffic control center, a sudden power surge occurs due to an external power source error. The UPS system is designed to handle moderate power fluctuations and provide temporary backup power. However, due to an inadequate UPS capacity or an error in the UPS configuration, the power surge overwhelms the UPS, causing it to fail.
In this scenario, the sudden loss of power and failure of the UPS result in a complete shutdown of critical systems within the control center. Communication channels go offline, radar systems cease to function, and the control center is left without the necessary tools to effectively manage air traffic. Air traffic controllers face significant challenges in maintaining situational awareness, coordinating aircraft movements, and ensuring safe separations. The lack of power and the failure of the UPS system severely disrupt air traffic control services, leading to extensive flight delays, increased workload for controllers, and potential safety risks.
These scenarios highlight the impact of power source errors related to UPS failures on air traffic control services. In both cases, the inability of the UPS system to provide backup power during a power outage or handle power surges can lead to communication disruptions, loss of surveillance capabilities, reduced situational awareness, and increased safety risks. To prevent such incidents, it is crucial to ensure UPS systems are properly configured, regularly maintained, and adequately sized to handle power demands. Regular testing, monitoring, and redundancy measures should be in place to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of the UPS system in supporting air traffic control operation.
To train various scenarios of power failure, SkyRadar's System Monitoring and Control Suite provides packages to simulate power failure and subsequent reaction of the UPS.
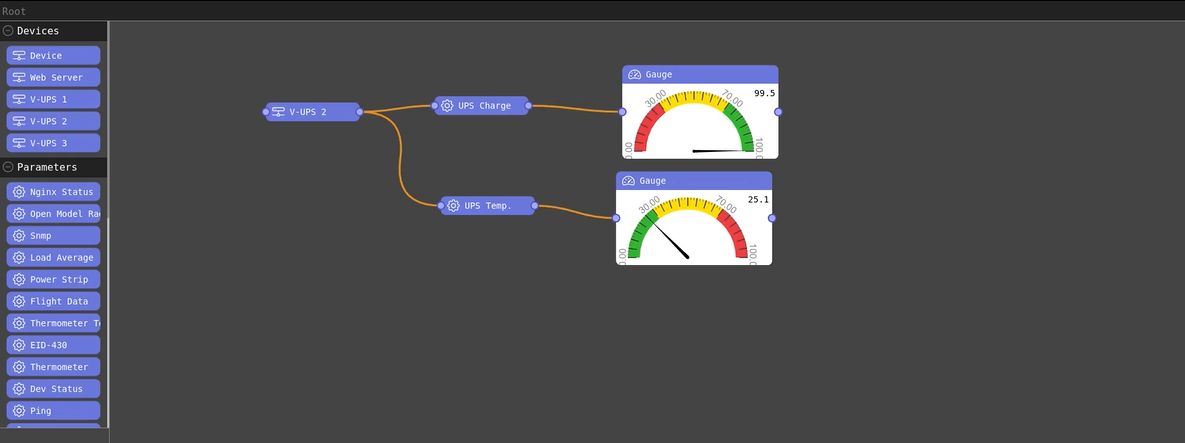
Impact of Power source errors related to UPS related errors on Air Traffic Control Services
Power source errors related to UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) failures can have a significant impact on air traffic control services. Here are some potential impacts
Communication Disruptions
Air traffic control services heavily rely on various communication systems, such as radios, data links, and telephone lines, to communicate with pilots and other air traffic control centers. When a power source error occurs, causing the UPS to fail, the loss of backup power can disrupt communication systems. Air traffic controllers may experience a loss of communication with pilots, hindering their ability to issue instructions, provide updates, and respond to emergency situations promptly.
Loss of Surveillance and Radar Systems
UPS failures can lead to a loss of power supply to critical systems, including radar and surveillance equipment. Without a stable power source, these systems may become inoperable, resulting in a loss of real-time data on aircraft positions, altitudes, and speeds. This loss of surveillance capability can severely impact the ability of air traffic controllers to monitor and manage airspace, increasing the risk of potential conflicts, reduced situational awareness, and compromised safety.
System Downtime and Operational Disruptions
Power source errors related to UPS failures can lead to system downtime and operational disruptions within air traffic control centers. If the primary power supply fails and the UPS is unable to provide backup power, essential systems and equipment may shut down. This can result in delays in flight operations, reduced airspace capacity, and increased workload for air traffic controllers
The operational efficiency of the air traffic control services is compromised, potentially causing cascading effects on neighboring sectors and airports.
Safety Risks
Power source errors related to UPS failures can introduce safety risks to air traffic control services. The loss of power and critical systems can hinder the ability of air traffic controllers to maintain safe aircraft separations, detect potential conflicts, and respond to emergency situations effectively. Safety incidents such as loss of separation, runway incursions, or miscommunication can occur, jeopardizing the safety of passengers and aircraft.
To mitigate the impact of power source errors related to UPS failures on air traffic control services, it is important to implement robust backup power systems, conduct regular maintenance and testing of UPS units, and establish contingency plans for power outages. Redundant power sources, such as backup generators or multiple UPS units, can help ensure uninterrupted power supply to critical systems. Regular training and drills for air traffic controllers can also enhance their ability to handle power source errors and maintain safe operations during challenging situations.
Factors Responsible for UPS related errors related Power Source Errors
Several factors can contribute to UPS related errors related to power source errors, including
Inadequate UPS capacity
If the UPS system is not adequately sized to handle the power requirements of critical systems, it may fail to provide adequate backup power in the event of a power outage.
Aging infrastructure
Aging infrastructure can contribute to UPS related errors by increasing the likelihood of equipment failure. As equipment ages, it becomes more prone to failure, which can result in power outages or disruptions in critical systems.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can impact the performance of UPS systems. High temperatures can lead to battery degradation, while high humidity can cause corrosion and other issues.
Lack of maintenance
Lack of regular maintenance can contribute to UPS related errors by allowing equipment to deteriorate and fail over time. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure that the UPS system is functioning correctly and providing adequate backup power to critical systems.
Some common types of Power Source Issues caused by UPS related errors
Some common types of power source errors caused by UPS related errors include:
Power Surges
UPS units may fail to regulate incoming voltage properly, resulting in sudden power surges that can damage sensitive equipment.
Voltage Fluctuations
UPS systems may experience voltage fluctuations, causing inconsistent power supply to connected devices and potentially disrupting their operation.
Battery Failures
UPS batteries can degrade over time or experience sudden failures, leading to a loss of backup power during electrical outages and compromising the reliability of critical systems.
Overloading
If the power demand exceeds the UPS capacity, it can lead to overloading, causing the UPS to shut down or supply insufficient power to connected devices.
Steps to be taken by ATSEP in Rectification of Power Source Issues related to UPS related errors
When ATSEPs (Air Traffic Safety Electronics Personnel) encounter power source errors related to UPS systems in air traffic control (ATC) facilities, they need to take prompt and effective steps to rectify the issues. Here are the detailed steps they can follow
Identify the Issue
Thoroughly investigate and diagnose the power source error related to the UPS system. Use monitoring tools, error logs, and diagnostic equipment to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
Isolate the Fault
Determine if the power source error is specific to the UPS unit or if it affects the entire power distribution system. Isolate the UPS from other equipment to focus on resolving the UPS-related error.
Check Connections
Inspect all electrical connections, including power cables, input/output connections, and grounding. Ensure that connections are secure, properly seated, and free from corrosion or damage.
Battery Inspection
Examine the UPS batteries for signs of damage, leakage, or swelling. Test the battery voltage, capacity, and health using appropriate tools. Replace faulty or aging batteries with new ones if necessary.
Firmware and Software Updates
Verify if the UPS firmware or software requires updates. Follow the manufacturer's instructions to install the latest updates, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility with other systems.
Troubleshooting and Error Resolution
Utilize troubleshooting guides, technical manuals, and support resources to identify specific solutions for the encountered power source error. Follow step-by-step procedures to rectify the issue based on the identified cause.
Repairs and Component Replacement
If a hardware fault is detected, repair or replace the faulty components or modules of the UPS system. Ensure that replacements are compatible and meet the manufacturer's specifications.
Calibration and Configuration
Perform necessary calibration and configuration adjustments as recommended by the UPS manufacturer. This includes settings related to voltage regulation, power factor correction, and battery charging.
Testing and Validation
After rectifying the power source error, thoroughly test the UPS system to ensure proper functionality and performance. Validate that the power source error has been resolved and that the UPS is operating as intended.
Documentation
Maintain comprehensive records of the encountered power source error, the steps taken for rectification, and any component replacements or repairs performed. Document the test results and ensure accurate and up-to-date maintenance records.
Preventive Measures
Review the incident and identify any preventive measures that can be implemented to avoid similar power source errors in the future. This may include implementing enhanced maintenance procedures, conducting regular inspections, or updating training programs.
Steps to be followed by ATSEP for preventing UPS related errors
ATSEPs (Air Traffic Safety Electronics Personnel) play a crucial role in preventing UPS-related errors and ensuring the reliable operation of UPS systems in air traffic control (ATC) facilities. Here are the steps they can follow to mitigate UPS-related errors:
Regular Inspections
Conduct routine inspections of UPS units to identify any signs of wear, damage, or potential issues. Inspect for loose connections, frayed cables, or any physical damage that may impact the UPS's performance.
Preventive Maintenance
Develop a preventive maintenance schedule for UPS systems, including regular battery checks, firmware updates, and component replacements. Follow manufacturer guidelines and best practices for maintenance tasks.
Battery Monitoring
Monitor the condition and performance of UPS batteries. Implement a battery testing program to assess battery health, capacity, and expected lifespan. Replace aging or faulty batteries promptly to avoid potential failures.
Environmental Considerations
Ensure that UPS units are placed in an appropriate environment with proper temperature and humidity control. Keep the UPS area clean and free from dust and debris, as environmental factors can impact UPS performance.
Load Management
Monitor the power load on UPS systems to prevent overloading. Regularly assess the power demands of connected devices and ensure that the UPS capacity is sufficient to handle the load. Avoid plugging in non-essential equipment that could strain the UPS.
Redundancy and Backup Plans
Implement redundant UPS systems or backup power sources to provide additional protection in case of UPS failures. Consider implementing automatic failover mechanisms to ensure uninterrupted power supply during critical operations.
Training and Awareness
Provide comprehensive training to ATSEP personnel on UPS systems, their maintenance, and troubleshooting procedures. Educate them on potential UPS-related errors, their impact on ATC operations, and the steps to address them effectively.
Documentation and Records
Maintain accurate records of UPS maintenance activities, including inspections, repairs, and battery replacements. Keep a log of any UPS-related errors or issues encountered, along with the actions taken for resolution.
Collaboration with Manufacturers and Experts
Stay informed about UPS system advancements and updates by collaborating with manufacturers, industry experts, and regulatory bodies. Stay up-to-date with the latest guidelines, recommendations, and best practices related to UPS maintenance and operation.
Research Highlights
Research on power source issues related to UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems and their impact on various industries, including air traffic control, has yielded several important findings. Here are some general research highlights related to power source issues and UPS related errors:
Frequency and Causes
Studies have identified that power source issues, including UPS related errors, are relatively common across industries. The causes can range from component failure and improper maintenance to electrical grid disruptions and power surges.
Impact on Critical Systems
Power source issues can have severe consequences on critical systems, such as air traffic control. Research has shown that UPS related errors can lead to power interruptions, system failures, and disruption of vital services, potentially compromising safety and operational efficiency.
Economic Implications
Power source issues can result in significant economic losses. Research has estimated the cost of power outages and UPS related errors, including lost productivity, equipment damage, and downtime, which can amount to millions of dollars.
Importance of UPS Maintenance
Studies emphasize the significance of regular UPS maintenance to prevent power source issues. Proper inspection, testing, and servicing of UPS systems can help identify and rectify potential problems before they cause disruptions.
Impact of Technology
Research highlights the role of advanced technologies in mitigating power source issues. Innovations such as smart monitoring systems, predictive maintenance, and automated fault detection help proactively manage UPS related errors and ensure continuous power supply.
Training and Awareness
Studies underscore the importance of training programs and awareness campaigns for personnel responsible for UPS systems. Adequate knowledge and skills in troubleshooting, maintenance, and error resolution are crucial for minimizing power source issues.
Collaboration and Standards
Research emphasizes the need for collaboration between industry stakeholders, including UPS manufacturers, power utility companies, and regulatory bodies, to establish standards and best practices for power source management. Consistent guidelines ensure the reliability and compatibility of UPS systems.
Wrapping up
The power source errors related to UPS systems can have serious implications for air traffic control systems. By taking steps to prevent and rectify these errors, ATSEP can help ensure the safety and efficiency of air traffic control operations. Some key steps that can be taken include regularly monitoring the UPS system, testing backup power sources, conducting routine maintenance on batteries and other components, and ensuring that proper procedures are in place for responding to power source errors. It is also important to invest in high-quality UPS systems that are designed specifically for the needs of air traffic control operations.
Moreover it is crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in UPS technology and best practices for power source management in air traffic control. By staying informed and implementing the most effective solutions, ATSEP can help minimize the risk of power source errors and ensure the ongoing safety and reliability of air traffic control systems.
SkyRadar's System Monitoring & Control Solution
SkySMC - SkyRadar’s System Monitoring and Control Suite is a pedagogically enhanced, fully operational monitoring & control tool. We have optimized it to cater for the ATSEP-SMC training compliant to EASA's Easy Access Rules for ATM-ANS (Regulation (EU) 2017/373) and ICAO Doc 10057.
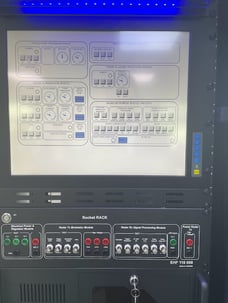

SkyRadar provides SkySMC as a complete laboratory in a turn-key approach, or as a service.
SkySMC is not a simulator, but a fully operational open monitoring system. It comes by default with a server including various virtualized applications and virtualized servers, but also connects to simulated systems. In addition, there are various hardware extensions available including training infrastructures, monitorable training radars, or even complete ATM systems, all connected to the System Monitoring & Control solution. Most components such as the radars, it IT infrastructure or networks exist in hardware and software (virtualized or simulated). The two photos above show the same socket panel in real hardware and in the simulator (fully functioning).
SkyRadar's System Monitoring & Control training system can be easily blended into distance learning solutions.
Let's talk
Stay tuned to be always the first to learn about new use cases and training solutions in radar qualification (real radars or simulators) for ATSEP.
Or simply talk to us to discuss your training solution.
References
Federal Aviation Administration. (2019). AC 150/5345-43J - Specification for Obstruction Lighting Equipment.
International Civil Aviation Organization. (2019). Annex 10 to the Convention on International Civil Aviation - Aeronautical Telecommunications, Volume I, Radio Navigation Aids.




